
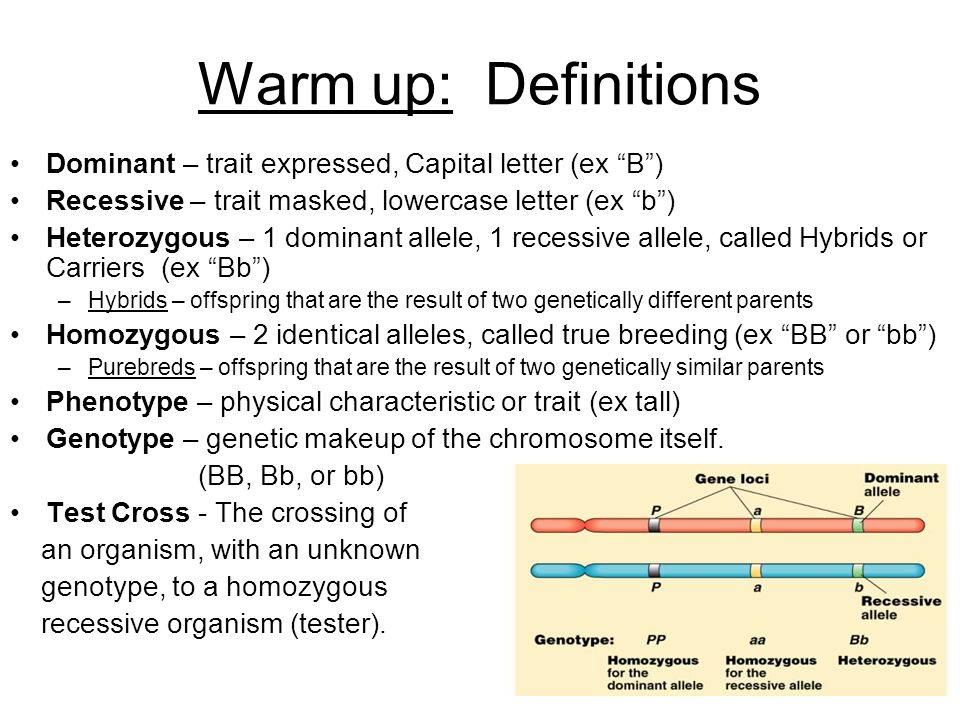
The recessive chromosome is represented as Xr. The ~ phase in the gymnosperm life cycle is the diploid (sporophyte) stage the gametophytes are very small and cannot exist independent of the parent plant. ~ allele any allele that is always expressed in the phenotype of an organism.ĭouble circulation a type of circulatory system in which blood passes through the heart twice during its journey around the body.ĭown's syndrome a genetic disorder in humans caused by the presence of an additional chromosome. ~: A genetic characteristic that is always expressed by the organismĮarthquake: The movement of Earth's plates which results in shaking on the surface of the crust. The haploid gametophyte is much smaller and simpler in structure. In ferns, both the sporophyte and the gametophyte are capable of living independently, but the ~ form is the diploid sporophyte. Microsatellites are co ~ genetic markers, because one can distinguish a heterozygote (two bands) from each of the homozygotes (single band). The phenotype is indistinguishable from that of homozygous ~ mutation.Ĭo ~: expression of heterozygote phenotypes that differ from either homozygote phenotype. ~-negative mutation: A (heterozygous) ~ mutation on one allele blocking the activity of wild-type protein still encoded by the normal allele (often by dimerising with it) causing a loss-of-function phenotype. ~ An allele that produces the same character whether present in the homozygous or heterozygous state. Considering a pair of homologous chromosomes containing a gene with two different alleles, how many different genotypes can that individual present? ~ Refers to an allele of a gene that is always expressed in heterozygotes.ġ3. If both alleles are detected, then co- ~. A ~ phenotype is detectable when only one variant allele can be detected. Nature of inheritance of a phenotype, not a gene. The second allele of the pair is considered recessive. ~ A relative term describing the relationship of one allele to a second at the same locus when an animal heterozygous for these alleles expresses the same phenotype as an animal homozygous for the first allele. ~ allele An allele which is expressed when only one copy is present in an individual, i.e., in heterozygous condition.Įcosystem The totality of all plant and animal species that constitute an interdepent, interrelated community.

(Adapted from Edexcel GCSE SCience and Data Resource Book, UG005206)Ģ) An allele that produces the same phenotype whether its paired allele is identical or different. ~: (as refers to gene action) the allele that masks the effect of another allele when present in a heterozygote state.įertilization: the union of male and female gametes to form a zygote, initiating biological reproduction.ġ) An allele which is always expressed in an individual.

The gene whose phenotype is expressed is the ~ allele and the allele whose phenotype is masked is the recessive allele. The phenotype that is observed when two alleles of a gene are present in a cell. Recessive: Requires inheritance of two copies of a gene to exhibit a traitĬarried: Genes that an individual possesses without exhibiting a trait. ~: Requires inheritance of only one copy of a gene to exhibit a trait In many cases, genotypic interactions between the two alleles at a locus can be described as ~ or recessive, ac cording to which of the two homozygous phenotypes the heterozygote most resembles. © All SSC BSL Glossary videos are Intellectual property of University of Edinburgh and cannot be used elsewhere without express permission of the Head of the Scottish Sensory Centre, Dr John Ravenscroft. The gene codes for a protein that makes dark pigment. Take rock pocket mice, where fur color is controlled mainly by a single gene. Mode of inheritance has nothing to do with whether an allele benefits an individual or not.

~ alleles are not better than recessive alleles
#DOMINANT TRAITS DEFINITION BIOLOGY PROFESSIONAL#
You can view samples of our professional work here. This is not an example of the work written by our professional essay writers. ĭisclaimer: This essay has been submitted by a student. The allele that is expressed when present in the heterozygote Also referring to the phenotype associated with a dominant allele. In genetics, referring to that allele of a gene expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygote the nonexpressed allele is recessive. Dominant ( biology definition): In genetics, it describes an allele or a gene that is expressed in an organism's phenotype, masking the effect of the recessive allele or gene when present it may also describe the trait or character that is expressed over the one that is not expressed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
